
We’ve recently launched a brand new website for KPT Solutions Ltd – a trusted supplier to the construction industry with a huge range of equipment available to buy or hire.
KPT came to Designer Websites looking for a complete overhaul of their online ordering system. Their brief was clear: create a website that feels right for the construction sector while also being sleek, modern and simple to use.
The new platform needed to…
- Make it easy to browse a large sales and hire range on any device
- Provide customers with robust online accounts for managing orders and hired items
- Integrate seamlessly with KPT’s existing ERP system
Visit www.kptsolutions.co.uk to see the new KPT website for yourself, or read on for a quick overview of what went into this project.
More...

If your website is 5+ years old, there’s a good chance it still “does the job”… but there’s also a good chance it’s quietly holding your business back.
And we don’t just mean the design looking a bit dated (although that’s usually part of it). The bigger issue is what’s happening under the bonnet: because technology moves fast, older websites are running on older frameworks and outdated code structures. This means that those older sites often inefficiently deliver content to modern browsers and mobile devices.
More...

Supplements Direct has been a familiar name in the UK fitness world for years – the place you'd go for your protein, creatine and so on. But as their customers' needs evolved beyond the gym, so did their brand. They wanted to move from being 'just' a sports supplement retailer to a trusted destination for everyday vitamins, health and wellbeing.
That's where we came in. Designer Websites were asked to create a new ecommerce website that would...
- Look clean and credible to a broader audience (without alienating the fitness-focused customer base)
- Provide a smooth shopping experience for mobile and desktop users
- Encourage repeat orders for daily vitamins and health supplements
- Perform brilliantly in search engines
And that's exactly what we built! Visit www.supplementsdirect.com now to see the results for yourself, or read on to learn more about this project.
More...
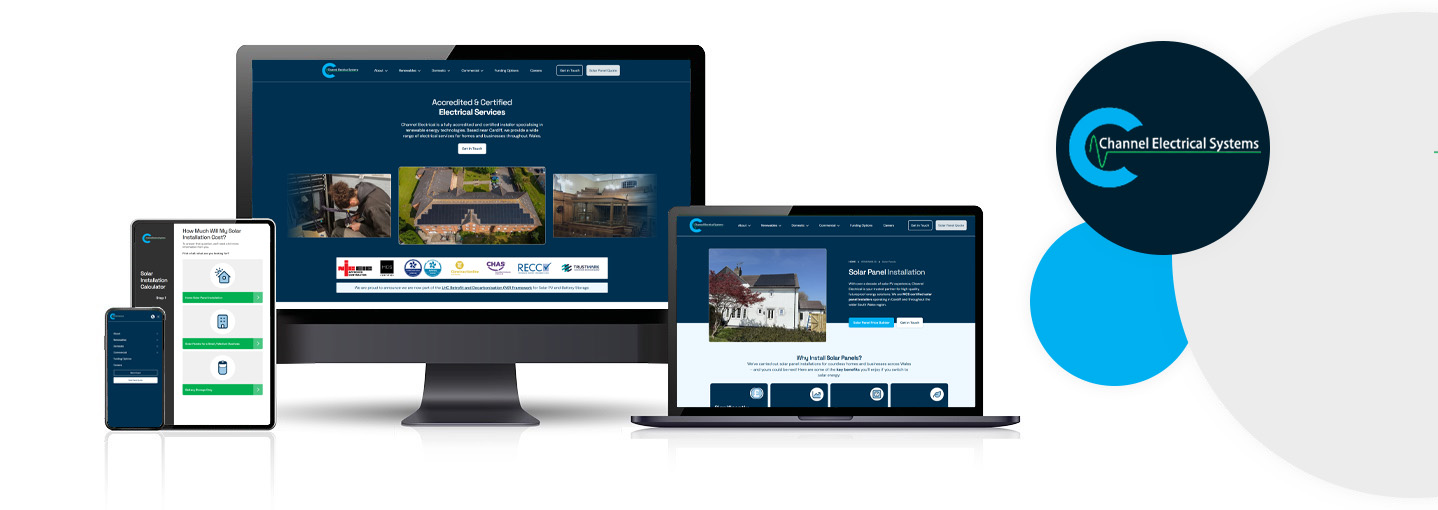
We've just launched a new website for Channel Electrical Systems, a team of renewable energy specialists who carry out electrical installations all over Wales.
The new website is a modern, user-friendly online platform that's designed to...
- Showcase the company's domestic and commercial electrical services
- Build trust with potential customers
- Make it quick and easy to get a price estimate for solar panel installation
Read on to learn more about this project!
More...

Established in 2010, NewBold Solicitors are among the UK's top property and housing law firms. They provide cost-effective and jargon-free legal assistance to landlords and other clients throughout both England and Wales.
NewBold came to us because they wanted their new website to reflect their professionalism and passion for client-centric legal advice. Their old website was last updated in 2018, and it lacked the personal and inviting feeling that these friendly solicitors want to give off.
More...